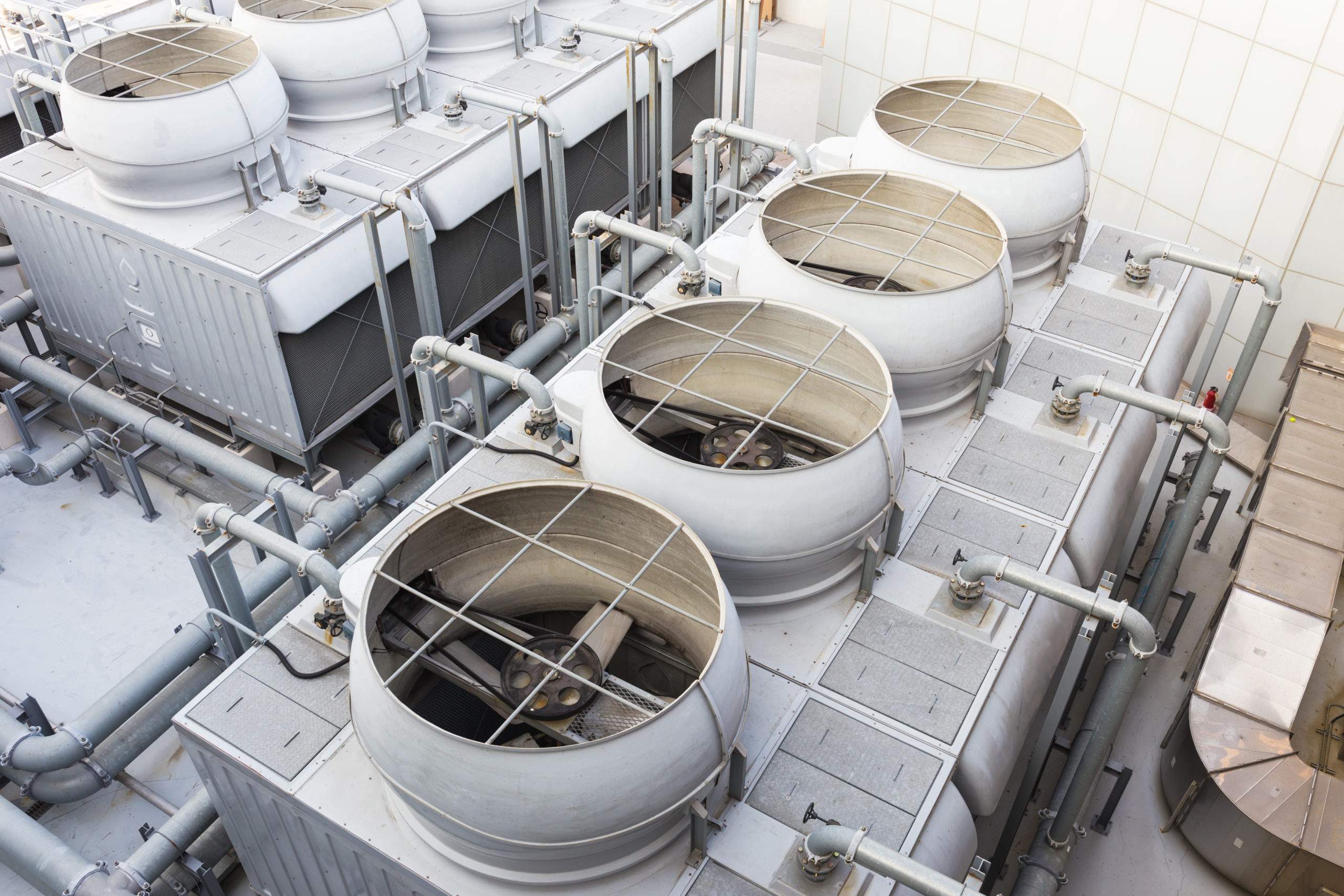
In response to a 2019 legionnaires’ disease outbreak in Moncton where fifteen people were hospitalized, the New Brunswick government has introduced legislation to reduce the risk of legionnaires’ disease in cooling towers. This bill was introduced by Health Minister Dorothy Shephard and would require a registry and associated maintenance and testing of cooling towers. The registry is meant to help quickly locate the towers for testing in the event of future outbreaks. Public Health officials have said that regular testing and maintenance can reduce the risk of bacteria; however, to this point there was nothing requiring such work in New…